
This is a checklist of 8 things you as a webmaster or owner of a WordPress site can do to improve SEO and search engine ranking in 2020.
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is a set of rules and guidelines for optimizing your website in order to achieve higher ranking in search engines. In today’s digital landscape SEO and SEO marketing is more important than ever. Search engines serve millions of users per day looking for answers to their questions or solutions to their problems. And you want people to find your site, right? Then you need to get your site as high up as possible in the search engine results!
1. Install a SEO plugin
The first best (and obvious) thing you can do to improve SEO on your site is installing a SEO plugin. With a SEO plugin you get features like defining page title, description and keywords for each page. The plugin should also be able to generate search engine sitemaps.
Yoast SEO is the largest and most known SEO plugin at the WordPress plugin market today. It has a premium version but you get most of the functionality in the free version. With Yoast SEO you can define keywords, customize page title, meta description, and it also analyzes your post content and gives you feedback on how to improve.
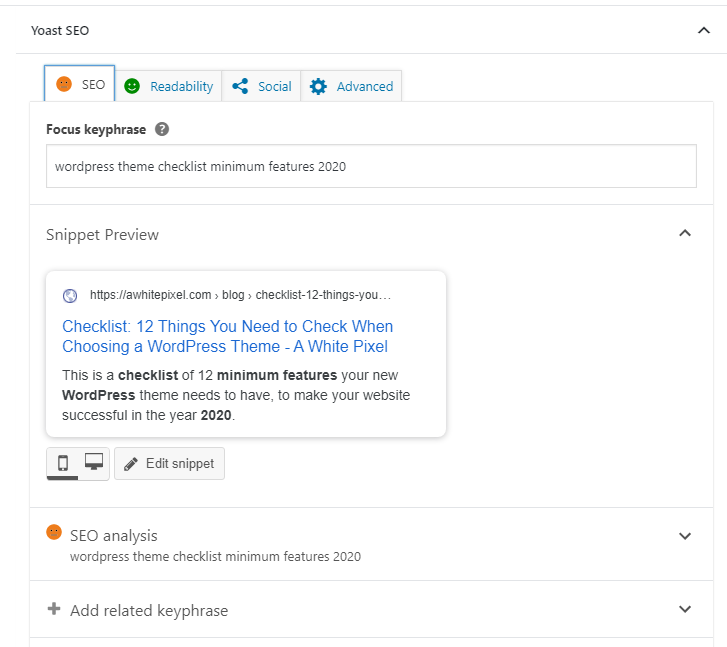
Other alternatives to free SEO plugins are SEOPress, All in One SEO Pack, and Rank Math.
2. Make sure your site is mobile-friendly
Today more than half of all website visits all over the world happen through a mobile device. Google picked this trend up already in 2015 and changed its algorithm to rank mobile-friendly sites much higher. Pages not optimized for mobile are today filtered out or seriously down-ranked. Also in Google has announced that they will switch to mobile-first indexing for all websites in September 2020.
Make sure your WordPress theme is responsive (styling that adjusts according to screen size). You can easily check it by dragging the right edge of your browser on your computer inwards. The content should start to stack on top of each other and the main menu should convert into a mobile menu button. No content should ever be hidden to the right “outside the screen”, behind a horizontal scrollbar. If your site is rocking a non-responsive design that isn’t mobile-friendly get a new theme as soon as possible!
You can use Google’s free tool to confirm that your site is mobile-friendly: Google’s mobile-friendly test. Type in your URL and click Test. If it reports back that it’s mobile-friendly, you’re good to go!
3. Add SSL
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) are protocols for authenticated and encrypted communication between two computers or servers. To put it very simply adding SSL to a site is making it more secure. It makes your site get https:// instead of http:// in the URL – and it adds the “secure lock” icon found in most known browsers.

You should never enter your credit card details or other sensitive information to a site that is unsecured (http://). Today most browsers will actually alert you when visiting an unsecure site. And accordingly Google’s search algorithms favor secure sites.
The process of adding SSL to your site is investing in a SSL certificate. This is basically a file that you need to install on your website’s server. A SSL certificate is usually offered by your hosting provider, either for free or for a small fee. If you are looking for free but trusted certificates, I recommend the nonprofit provider Let’s Encrypt.
4. Improve pagespeed
The speed your website loads is among the most significant success factors websites face in SEO. Google and other search engines measure and factor in the speed in their ranking algorithm.
There are many ways to improve pagespeed and it depends on your site. Use Google’s free test tool PageSpeed Insights to analyze your site and get a detailed report on what you can do to improve.
Common things (but the most easy to fix) that drag down the pagespeed are;
- Large images. Make sure to optimize and rescale images to minimize their file size as much as possible or use alternative image files types. If you have a good image editing software like Photoshop, use its functions to export images to lower file size without loss of quality. There are multiple online image compressors you can use as well.
- External resources. Your site might request resources such as external font libraries (e.g. GoogleFonts), or other scripts or styles for site features, social media, or integrations. The problem is that your website has to wait for all of them to answer before the page can be rendered. See if you can avoid these – follow the hints provided by Google PageSpeed Insights.
- Too many large script and style files. A common problem with WordPress is that there can often be a lot of styles and script files. WordPress has its own, the theme has its own, and any plugins you have each have their own. In total it would be a lot of requests for styles and scripts. If this is a serious problem on your site, consider cutting down on un-used plugins or find ways to minimize these files if they are large in file size.
- Slow hosting provider. If you cheapen out on your hosting provider, you risk ending up with a provider that serve sites slow. The only way to go around this is investing in a good hosting provider.
A good strategy to increase website performance and reducing load times is using a cache plugin. I recommend the free cache plugin W3 Total Cache.
5. Good URL structure
A website’s URL structure matters. It serves as a way to inform the search engines of how important the different parts of your content is.
As minimum you should activate “pretty permalinks” in WordPress. In WordPress admin go to Settings > Permalinks. When you install WordPress it defaults to “Plain” URL’s, which look something like this: https://domain.com/?p=123. This is a no-go for SEO! I recommend choosing “Post name”. This generates a slug version of the post’s title in the URL.
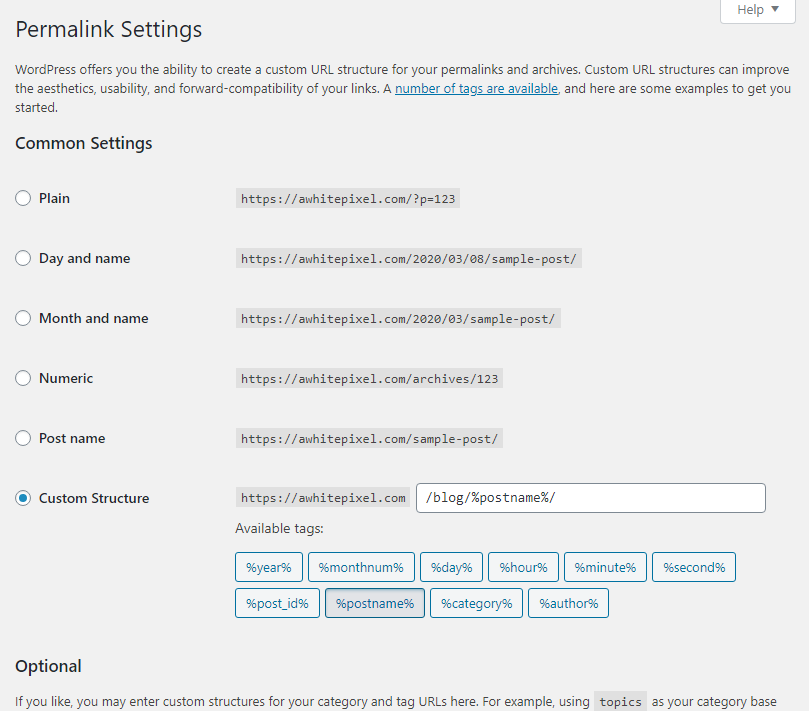
Keep in mind that you can edit the post’s URL slug. Search engines prefer shorter URL’s so keep the number of words in the slug to 5 or less. It’s also a good idea to include the keywords you want to rank for in the slug.
Search engines’s crawlers that read your site also look at the number of “directories” or the number of “/” away from the domain. What I mean by this is that an URL domain.com/fantastic-post is considered more important than domain.com/subfolder/fantastic-post, and that in turn is considered more important than domain.com/subfolder/anothersubfolder/fantastic-post.
Place your most important pages just one “directory” away from your domain (e.g. domain.com/fantastic-post). Avoid having URL structures down more than three levels.
6. Use Google Analytics and Google Search Console
How can you know how to improve SEO if you don’t track your current ranking and traffic? Google has two free and fantastic tools for SEO: Google Analytics and Google Search Console (previously named Google Webmaster Tools).
Google Analytics (GA) is a web service that tracks and reports website traffic. With this tool you get a lot of information about your site’s traffic, where they come from, how they found you, how long they spend on your site, and much, much more.
Google Search Console (GSC) is a web service that gives you information about the visibility of your site in search engines. With GSC you can track what people searched for before they clicked on your site, and how high in the search results your site appears.
All you need for both services is a Google account. When you create a new profile for your website on both tools, you get a code that you need to add to your website. This is easily solved by using a free plugin that inserts the GA and GSC codes, or by simply editing the theme header file. You will find plenty of guides online about how to do this.
After you have set up Google Search Console for your site you should submit your site’s sitemap. Your site should have a sitemap provided by your SEO plugin (see checklist item 1). Find its URL and submit this to Google Search Console. This makes it easier for Google to crawl your pages.
7. Optimize your writing
Finally keep in mind that search engines also look at how you write your content. The length of posts, use and frequency of (key)words, links, and content structuring such as subheadings. These days all that really matters is quality. Getting higher ranking by spamming keywords and dummy articles no longer work – they can actually hurt you.
The main takeaway here is to write quality content. There are some tweaks and guidelines you can keep in mind though. If you are interested in this topic there are pleny of litterature on how to copywrite (marketing) and how to write SEO optimized.
Some quick pointers
- Articles should be over 1000 words. Minimum.
- Do keyword research. Figure out what keywords you want to rank for. Don’t compete for keywords with a lot of competition. Target the long-tail keywords – which are keywords with quite a few words in it. Make sure your content contains the keywords, but don’t just sprinkle them around in illogical places.
- Use headings (
h1–h6) correctly. Theh1tag should be the most (and only) important title. Use subtitles (h2) for direct subtopics. Use keywords in the headings. Search engines do look forh1andh2, but actually don’t care much forh3–h6. But that doesn’t mean you should skimp on those. Use headings to make it easier to read by logically dividing up your content. - Don’t write too complicated. Make your text easy to read, and write personally (use of “you” and “me”). Vary sentence length to keep the text interesting to read, but don’t make them too long. (This is where I struggle!) Use paragraphs, headings and images to break up large chunks of text.
- You should add outbound links (links going out to other sites). Add at least 1-2 in each article. Links early in the article weighs more than links later in the text.
- Use internal links. You want to keep people staying on your site. By clever use of internal links Google also gets an idea of what pages on your site is important.
- Update your content frequently. Don’t just change one word in an article, but keep publishing new content regularly. Google favors “freshness” in content, as this is increased chance of more relevant and recent information than old and possibly outdated information.
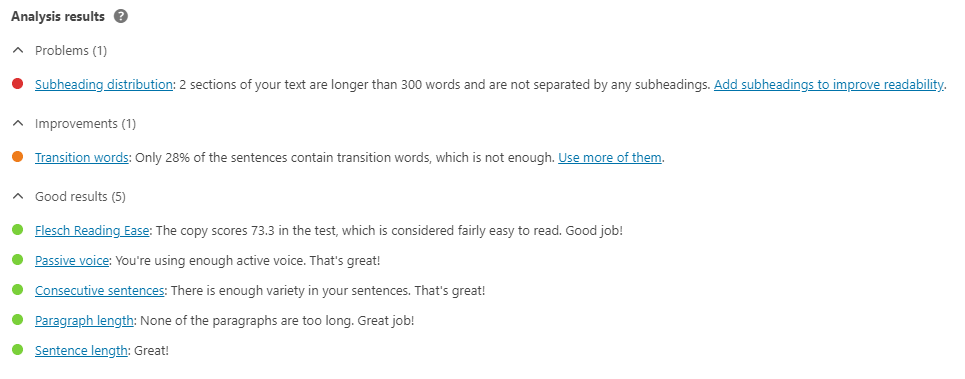
If you opted for Yoast SEO plugin (checklist item 1) the plugin will analyze your content and give you more tips on how to improve your writing. Most of them have a link to their site that explains the topic in depth and why this matters for SEO. As an example these are the tips they give me for this very article:
Conclusion
There is no one single way to drastically improving your SEO and ranking. SEO is a matter of checking a lot of checkboxes. Also it takes time. Don’t expect to get thousands of visitors the following day after doing some of the steps. But if you follow the above steps, keep improving and learning more, gradually your site should improve SEO-wise!
There are plenty of tools out there to give you an idea of how your site is doing. I recommend trying out WPMUDev’s free WordPress Checkup tool. Enter your WordPress URL and get a free report on topics like SEO, security, and performance.